This demo showcases how a sizing optimisation of a truss structure can be addressed. For this example we will optimise an inverse truss bridge design.
In particular this demo emphasizes
implementation of a linear elastic truss model with
ufl,creation of (braced) truss meshes, and
the interface to PETSc/TAO for optimisation solvers.
import argparse
from mpi4py import MPI
from petsc4py import PETSc
import dolfinx
import dolfinx.fem.petsc
import ufl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib_inline
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
import dolfiny
import dolfiny.taoproblemSource
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Truss sizing demo")
parser.add_argument(
"-a",
"--algorithm",
choices=["conlin", "mma"],
default="mma",
help="Choose optimisation algorithm",
)
args, _unknown = parser.parse_known_args()Generation of Truss Meshes¶
Truss structures make up an interesting example of the concept of geometric- and topological dimension, let those be denoted as and , which is also used throughout DOLFINx Baratta et al., 2023.
The geometric dimension is the dimension of the space in which the mesh is embedded, and , and the topological dimension is the dimension of the cells of the mesh in the reference configuration, for the reference cell of .
The usual finite element text-book setting applies to the case , for example a triangle mesh is only considered in and not in .
Trusses are made up of lines, or, domain inspecifc, intervals, which are one-dimensional entities and form planar or volumetric structures, . Here, we consider the volumetric case, .
The bridge dimensions (length, height, width) are all in meters and we create
the truss mesh from the edges of a (regular) hexahedral mesh, with trusses of size , and
introduce all possible bracings to it.
This is what the create_truss_x_braced_mesh functionality simplifies.
Given a hexehedral mesh, it generates the edge skeleton together with all possible bracings.
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
dim = np.array([100, 20, 10], dtype=np.float64)
elem_size = 5
mesh = dolfiny.mesh_generation.create_truss_x_braced_mesh(
dolfinx.mesh.create_box(
MPI.COMM_SELF,
[np.zeros_like(dim), dim],
(dim / elem_size).astype(np.int32), # type: ignore
dolfinx.mesh.CellType.hexahedron,
)
if comm.rank == 0
else None
)We create one functionspace for the displacement field and one for the cross sectional area of the trusses, which we model as constant over each element, so .
V_u = dolfinx.fem.functionspace(mesh, ("CG", 1, (3,)))
u = dolfinx.fem.Function(V_u, name="displacement")
V_s = dolfinx.fem.functionspace(mesh, ("DG", 0))
s = dolfinx.fem.Function(V_s, name="cross-sectional-area")Boundary Conditions and Load Surface¶
For the realisation of an inverse truss bridge, we will fix the trusses on the left and right top edges and apply a vertical load, i.e. in -direction, on the bridge deck, which we assume to span the whole upper surface/side of the truss mesh, excluding the fixed edges.
mesh.topology.create_connectivity(0, 1)
vertices_fixed = dolfinx.mesh.locate_entities(
mesh,
0,
lambda x: (np.isclose(x[0], 0) | np.isclose(x[0], dim[0])) & np.isclose(x[1], dim[1]),
)
dofs_fixed = dolfinx.fem.locate_dofs_topological(V_u, 0, vertices_fixed)
bcs = [dolfinx.fem.dirichletbc(np.zeros(3, dtype=np.float64), dofs_fixed, V_u)]
vertices_load = dolfinx.mesh.locate_entities(
mesh, 0, lambda x: np.isclose(x[1], dim[1]) & np.greater(x[0], 0) & np.less(x[0], dim[0])
)
meshtags = dolfinx.mesh.meshtags(mesh, 0, vertices_load, 1)
vertices_load_local = vertices_load[vertices_load < mesh.topology.index_map(0).size_local]Source
pv.set_jupyter_backend("static")
pv_grid = pv.UnstructuredGrid(*dolfinx.plot.vtk_mesh(mesh))
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[3840, 2160])
plotter.add_mesh(pv_grid, color="black", line_width=1.5)
for v in vertices_load:
v_coords = mesh.geometry.x[v]
arrow = pv.Arrow(start=v_coords + np.array([0, 4, 0]), direction=[0, -1, 0], scale=4)
plotter.add_mesh(arrow, color="green", opacity=0.5)
for v in vertices_fixed:
v_coords = mesh.geometry.x[v]
sphere = pv.Sphere(radius=0.5, center=v_coords)
plotter.add_mesh(sphere, color="red")
plotter.view_xy()
plotter.add_axes()
plotter.camera.elevation += 20
plotter.camera.zoom(1.7)
plotter.show()
plotter.close()
plotter.deep_clean()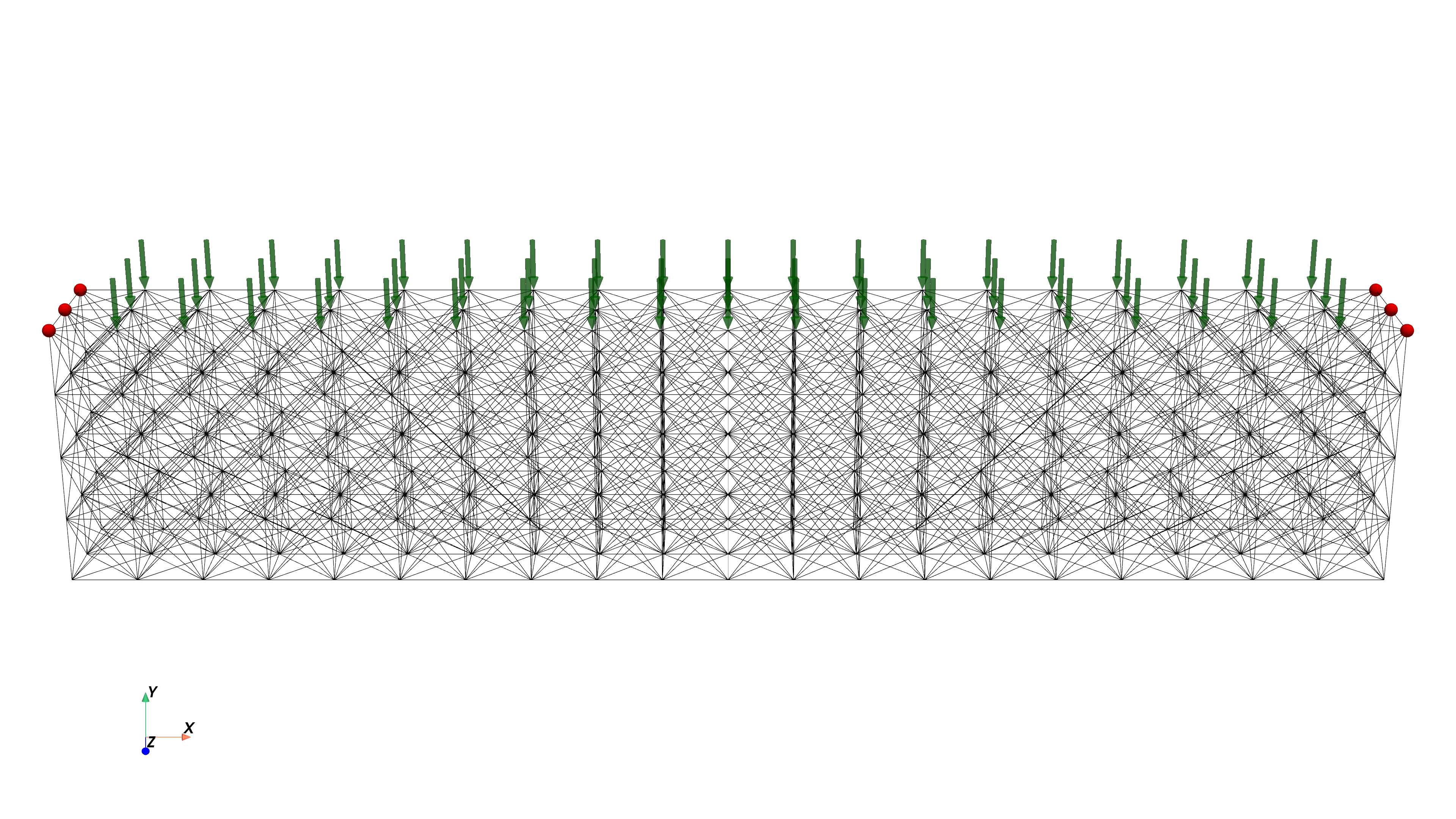
Truss Model and Forward Problem¶
We rely on a linear elastic truss model, same as the one presented in Bleyer, 2024. We choose a Young’s modulus of and apply a total load of , equally distributed across the loaded nodes.
tangent = ufl.Jacobian(mesh)[:, 0]
tangent /= ufl.sqrt(ufl.inner(tangent, tangent))
E = 200.0 * 1e9 # [E] = Pa = N/m^2
ε = ufl.dot(ufl.dot(ufl.grad(u), tangent), tangent) # strain
N = E * s * ε # normal_force
dP = ufl.Measure("dP", domain=mesh, subdomain_data=meshtags)
total_load = 300 * 1e3
num_load_vertices = comm.allreduce(vertices_load_local.size)
F = ufl.as_vector([0, -total_load / num_load_vertices, 0])
compliance = ufl.inner(F, u) * dP(1)
E = 1 / 2 * ufl.inner(N, ε) * ufl.dx - compliance
a = ufl.derivative(ufl.derivative(E, u), u)
L = ufl.derivative(compliance, u)
state_solver = dolfinx.fem.petsc.LinearProblem(
a,
L,
bcs=bcs,
u=u,
petsc_options={
"ksp_type": "preonly",
"pc_type": "lu",
"pc_factor_mat_solver_type": "mumps",
"ksp_error_if_not_converged": "True",
"mat_mumps_cntl_1": 0.0,
},
petsc_options_prefix="state_solver",
)Output
Optimisation of Cross-sectional Areas¶
The truss sizing optimisation problem from Christensen & Klarbring, 2009 we are interested in is given (in reduced form) by
where is the unique displacement field associated with a given sizing .
For the bounds of the truss cross sectional area we consider an upper bound of and set the the lower bound to .
compliance_form = dolfinx.fem.form(compliance)
@dolfiny.taoproblem.sync_functions([s])
def C(tao, x) -> float:
state_solver.solve()
return comm.allreduce(dolfinx.fem.assemble_scalar(compliance_form)) # type: ignore
# p = -u
p = dolfinx.fem.Function(V_u)
gx = dolfinx.fem.form(ufl.derivative(ufl.derivative(E, u, p), s))
@dolfiny.taoproblem.sync_functions([s])
def JC(tao, x, J):
state_solver.solve()
J.zeroEntries()
p.x.array[:] = -u.x.array
dolfinx.fem.petsc.assemble_vector(J, gx)
J.ghostUpdate(addv=PETSc.InsertMode.ADD, mode=PETSc.ScatterMode.REVERSE)
s_max = np.float64(1e-2)
s_min = np.float64(1e-3 * s_max)
max_vol = comm.allreduce(
dolfinx.fem.assemble_scalar(dolfinx.fem.form(dolfinx.fem.Constant(mesh, s_max) * ufl.dx))
)
volume_fraction = 1 / 20
h = [s / max_vol / volume_fraction * ufl.dx <= 1]
s.x.array[:] = 1 / 100 * s_max
opts = PETSc.Options("truss") # type: ignore
opts["tao_type"] = "python"
opts["tao_monitor"] = ""
opts["tao_max_it"] = (max_it := 50)
if args.algorithm == "conlin":
opts["tao_python_type"] = "dolfiny.conlin.CONLIN"
else: # mma
opts["tao_python_type"] = "dolfiny.mma.MMA"
opts["tao_mma_move_limit"] = 0.05
opts["tao_mma_subsolver_tao_max_it"] = 30
problem = dolfiny.taoproblem.TAOProblem(
C, [s], bcs=bcs, J=(JC, s.x.petsc_vec.copy()), h=h, lb=s_min, ub=s_max, prefix="truss"
)
def monitor(tao, comp, volume):
it = tao.getIterationNumber()
comp[it] = tao.getObjectiveValue()
volume[it] = dolfinx.fem.assemble_scalar(dolfinx.fem.form(h[0].lhs))
comp = np.zeros(max_it, np.float64)
volume = np.zeros(max_it, np.float64)
if comm.size == 1:
problem.tao.setMonitor(monitor, (comp, volume))
problem.solve()
state_solver.solve()Output
Iteration information for truss solve.
0 TAO, Function value: 19614.4, Residual: 0.
# TAO 0 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=5.117e-03 |J|=1.025e+07 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=5.117e-03 |J|=1.025e+07 |h|=0.000e+00 |Jh|=0.000e+00 f=1.961e+04
1 TAO, Function value: 3315.56, Residual: 289728.
# TAO 1 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=2.680e-02 |J|=2.897e+05 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=2.680e-02 |J|=2.897e+05 |h|=8.000e-01 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=3.316e+03
2 TAO, Function value: 2142.44, Residual: 121362.
# TAO 2 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=3.489e-02 |J|=1.214e+05 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=3.489e-02 |J|=1.214e+05 |h|=8.368e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=2.142e+03
3 TAO, Function value: 1648.92, Residual: 77696.9
# TAO 3 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=3.923e-02 |J|=7.770e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=3.923e-02 |J|=7.770e+04 |h|=6.729e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=1.649e+03
4 TAO, Function value: 1390.03, Residual: 80160.9
# TAO 4 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=4.556e-02 |J|=8.016e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=4.556e-02 |J|=8.016e+04 |h|=5.449e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=1.390e+03
5 TAO, Function value: 1223.78, Residual: 42986.3
# TAO 5 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=4.995e-02 |J|=4.299e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=4.995e-02 |J|=4.299e+04 |h|=4.857e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=1.224e+03
6 TAO, Function value: 1109.08, Residual: 50835.4
# TAO 6 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=5.493e-02 |J|=5.084e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=5.493e-02 |J|=5.084e+04 |h|=4.832e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=1.109e+03
7 TAO, Function value: 1025.34, Residual: 26288.2
# TAO 7 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=5.791e-02 |J|=2.629e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=5.791e-02 |J|=2.629e+04 |h|=3.917e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=1.025e+03
8 TAO, Function value: 932.513, Residual: 26873.7
# TAO 8 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=6.400e-02 |J|=2.687e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=6.400e-02 |J|=2.687e+04 |h|=3.706e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=9.325e+02
9 TAO, Function value: 884.561, Residual: 19086.1
# TAO 9 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=6.679e-02 |J|=1.909e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=6.679e-02 |J|=1.909e+04 |h|=2.624e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=8.846e+02
10 TAO, Function value: 831.9, Residual: 17213.2
# TAO 10 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=7.119e-02 |J|=1.721e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=7.119e-02 |J|=1.721e+04 |h|=1.803e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=8.319e+02
11 TAO, Function value: 801.734, Residual: 18340.9
# TAO 11 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=7.406e-02 |J|=1.834e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=7.406e-02 |J|=1.834e+04 |h|=1.140e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=8.017e+02
12 TAO, Function value: 786.914, Residual: 16978.9
# TAO 12 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=7.550e-02 |J|=1.698e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=7.550e-02 |J|=1.698e+04 |h|=6.276e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.869e+02
13 TAO, Function value: 763.783, Residual: 15603.5
# TAO 13 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=7.800e-02 |J|=1.560e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=7.800e-02 |J|=1.560e+04 |h|=7.674e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.638e+02
14 TAO, Function value: 748.808, Residual: 27330.8
# TAO 14 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=8.042e-02 |J|=2.733e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=8.042e-02 |J|=2.733e+04 |h|=7.190e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.488e+02
15 TAO, Function value: 751.909, Residual: 16953.3
# TAO 15 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=7.972e-02 |J|=1.695e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=7.972e-02 |J|=1.695e+04 |h|=5.554e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.519e+02
16 TAO, Function value: 726.702, Residual: 16158.5
# TAO 16 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=8.286e-02 |J|=1.616e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=8.286e-02 |J|=1.616e+04 |h|=1.256e-02 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.267e+02
17 TAO, Function value: 713.137, Residual: 15300.6
# TAO 17 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=8.459e-02 |J|=1.530e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=8.459e-02 |J|=1.530e+04 |h|=9.076e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.131e+02
18 TAO, Function value: 702.44, Residual: 15307.7
# TAO 18 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=8.625e-02 |J|=1.531e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=8.625e-02 |J|=1.531e+04 |h|=6.239e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=7.024e+02
19 TAO, Function value: 690.009, Residual: 13636.7
# TAO 19 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=8.817e-02 |J|=1.364e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=8.817e-02 |J|=1.364e+04 |h|=6.252e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.900e+02
20 TAO, Function value: 679.203, Residual: 12897.3
# TAO 20 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.017e-02 |J|=1.290e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.017e-02 |J|=1.290e+04 |h|=5.602e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.792e+02
21 TAO, Function value: 675.623, Residual: 12722.1
# TAO 21 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.085e-02 |J|=1.272e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.085e-02 |J|=1.272e+04 |h|=4.684e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.756e+02
22 TAO, Function value: 675.236, Residual: 12819.9
# TAO 22 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.095e-02 |J|=1.282e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.095e-02 |J|=1.282e+04 |h|=3.681e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.752e+02
23 TAO, Function value: 673.486, Residual: 11504.3
# TAO 23 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.136e-02 |J|=1.150e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.136e-02 |J|=1.150e+04 |h|=3.492e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.735e+02
24 TAO, Function value: 671.741, Residual: 11977.9
# TAO 24 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.168e-02 |J|=1.198e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.168e-02 |J|=1.198e+04 |h|=3.710e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.717e+02
25 TAO, Function value: 672.325, Residual: 11052.9
# TAO 25 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.173e-02 |J|=1.105e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.173e-02 |J|=1.105e+04 |h|=2.905e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.723e+02
26 TAO, Function value: 669.717, Residual: 11892.2
# TAO 26 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.207e-02 |J|=1.189e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.207e-02 |J|=1.189e+04 |h|=2.930e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.697e+02
27 TAO, Function value: 671.428, Residual: 11061.6
# TAO 27 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.192e-02 |J|=1.106e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.192e-02 |J|=1.106e+04 |h|=2.255e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.714e+02
28 TAO, Function value: 668.967, Residual: 13043.8
# TAO 28 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.232e-02 |J|=1.304e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.232e-02 |J|=1.304e+04 |h|=2.630e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.690e+02
29 TAO, Function value: 671.666, Residual: 11109.6
# TAO 29 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.202e-02 |J|=1.111e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.202e-02 |J|=1.111e+04 |h|=2.285e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.717e+02
30 TAO, Function value: 668.425, Residual: 12137.9
# TAO 30 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.251e-02 |J|=1.214e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.251e-02 |J|=1.214e+04 |h|=3.350e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.684e+02
31 TAO, Function value: 668.046, Residual: 10600.1
# TAO 31 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.254e-02 |J|=1.060e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.254e-02 |J|=1.060e+04 |h|=2.472e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.680e+02
32 TAO, Function value: 667.11, Residual: 11092.2
# TAO 32 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.270e-02 |J|=1.109e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.270e-02 |J|=1.109e+04 |h|=1.509e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.671e+02
33 TAO, Function value: 667.134, Residual: 11017.6
# TAO 33 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.270e-02 |J|=1.102e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.270e-02 |J|=1.102e+04 |h|=9.261e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.671e+02
34 TAO, Function value: 668.263, Residual: 11184.8
# TAO 34 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.261e-02 |J|=1.118e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.261e-02 |J|=1.118e+04 |h|=5.980e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.683e+02
35 TAO, Function value: 667.581, Residual: 10950.2
# TAO 35 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.269e-02 |J|=1.095e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.269e-02 |J|=1.095e+04 |h|=1.029e-03 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.676e+02
36 TAO, Function value: 667.153, Residual: 10822.1
# TAO 36 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.275e-02 |J|=1.082e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.275e-02 |J|=1.082e+04 |h|=9.733e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.672e+02
37 TAO, Function value: 666.849, Residual: 10733.5
# TAO 37 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.281e-02 |J|=1.073e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.281e-02 |J|=1.073e+04 |h|=7.591e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.668e+02
38 TAO, Function value: 666.431, Residual: 10607.4
# TAO 38 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.288e-02 |J|=1.061e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.288e-02 |J|=1.061e+04 |h|=6.380e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.664e+02
39 TAO, Function value: 666.256, Residual: 10584.2
# TAO 39 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.292e-02 |J|=1.058e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.292e-02 |J|=1.058e+04 |h|=4.288e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.663e+02
40 TAO, Function value: 666.078, Residual: 10398.2
# TAO 40 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.295e-02 |J|=1.040e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.295e-02 |J|=1.040e+04 |h|=3.030e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.661e+02
41 TAO, Function value: 665.969, Residual: 10287.8
# TAO 41 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.296e-02 |J|=1.029e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.296e-02 |J|=1.029e+04 |h|=2.525e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.660e+02
42 TAO, Function value: 665.898, Residual: 10230.6
# TAO 42 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.298e-02 |J|=1.023e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.298e-02 |J|=1.023e+04 |h|=1.225e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
43 TAO, Function value: 665.936, Residual: 10273.4
# TAO 43 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.301e-02 |J|=1.027e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.301e-02 |J|=1.027e+04 |h|=7.149e-05 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
44 TAO, Function value: 666.018, Residual: 10201.1
# TAO 44 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.296e-02 |J|=1.020e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.296e-02 |J|=1.020e+04 |h|=6.749e-05 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.660e+02
45 TAO, Function value: 665.935, Residual: 10253.9
# TAO 45 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.302e-02 |J|=1.025e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.302e-02 |J|=1.025e+04 |h|=2.009e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
46 TAO, Function value: 665.865, Residual: 10229.6
# TAO 46 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.302e-02 |J|=1.023e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.302e-02 |J|=1.023e+04 |h|=1.783e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
47 TAO, Function value: 665.882, Residual: 10353.1
# TAO 47 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.304e-02 |J|=1.035e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.304e-02 |J|=1.035e+04 |h|=9.636e-05 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
48 TAO, Function value: 665.979, Residual: 10320.7
# TAO 48 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.306e-02 |J|=1.032e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.306e-02 |J|=1.032e+04 |h|=9.086e-05 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.660e+02
49 TAO, Function value: 665.892, Residual: 10332.6
# TAO 49 (ITERATING)
# sub 0 [ 2k] |x|=9.310e-02 |J|=1.033e+04 (cross-sectional-area)
# all |x|=9.310e-02 |J|=1.033e+04 |h|=2.063e-04 |Jh|=3.984e+01 f=6.659e+02
Coefficient(FunctionSpace(Mesh(blocked element (Basix element (P, interval, 1, gll_warped, unset, False, float64, []), (3,)), 1), blocked element (Basix element (P, interval, 1, gll_warped, unset, False, float64, []), (3,))), 0)Source
# verify result
# if problem.tao.getConvergedReason() <= 0:
# raise RuntimeError("Optimisation did not converge.")
if (
np.abs(comm.allreduce(dolfinx.fem.assemble_scalar(dolfinx.fem.form(h[0].lhs))) - h[0].rhs)
>= 1e-2
):
raise RuntimeError("Volume constraint violated.")
if np.any(s.x.array < s_min):
raise RuntimeError("Lower bound violated.")
if np.any(s.x.array > s_max):
raise RuntimeError("Upper bound violated.")
with dolfinx.io.VTXWriter(comm, "S.bp", s, "bp4") as file:
file.write(0.0)
with dolfinx.io.VTXWriter(comm, "u.bp", u, "bp4") as file:
file.write(0.0)
if comm.size > 1:
exit()Convergence of the optimisation, that is the compliance and the volume vs. outer MMA iteration are shown below. Compliance is measured relative to the initial compliance , which is compliance for the initial guess of . Volume is shown relative to the upper bound .
Source
matplotlib_inline.backend_inline.set_matplotlib_formats("png")
it = problem.tao.getIterationNumber()
comp = comp[:it]
volume = volume[:it]
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(dpi=400)
ax1.set_xlim(0, it - 1)
ax1.set_xlabel("Outer MMA iteration")
ax1.set_ylabel("Rel. compliance $C / C_0$")
plt_compliance = ax1.plot(
np.arange(0, it, dtype=int),
comp / comp[0],
color="tab:orange",
marker="x",
)
ax1.set_yscale("log")
ax1.grid(True, which="both")
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
ax2.set_ylabel(r"$|1 - V / V_\text{max}|$")
plt_volume = ax2.plot(np.arange(0, it, dtype=int), np.abs(1 - volume / h[0].rhs), marker=".")
ax2.axhline(y=1, linestyle="--")
ax2.set_yscale("log")
ax1.legend(plt_compliance + plt_volume, ["compliance", "volume"], loc=7)
plt.show()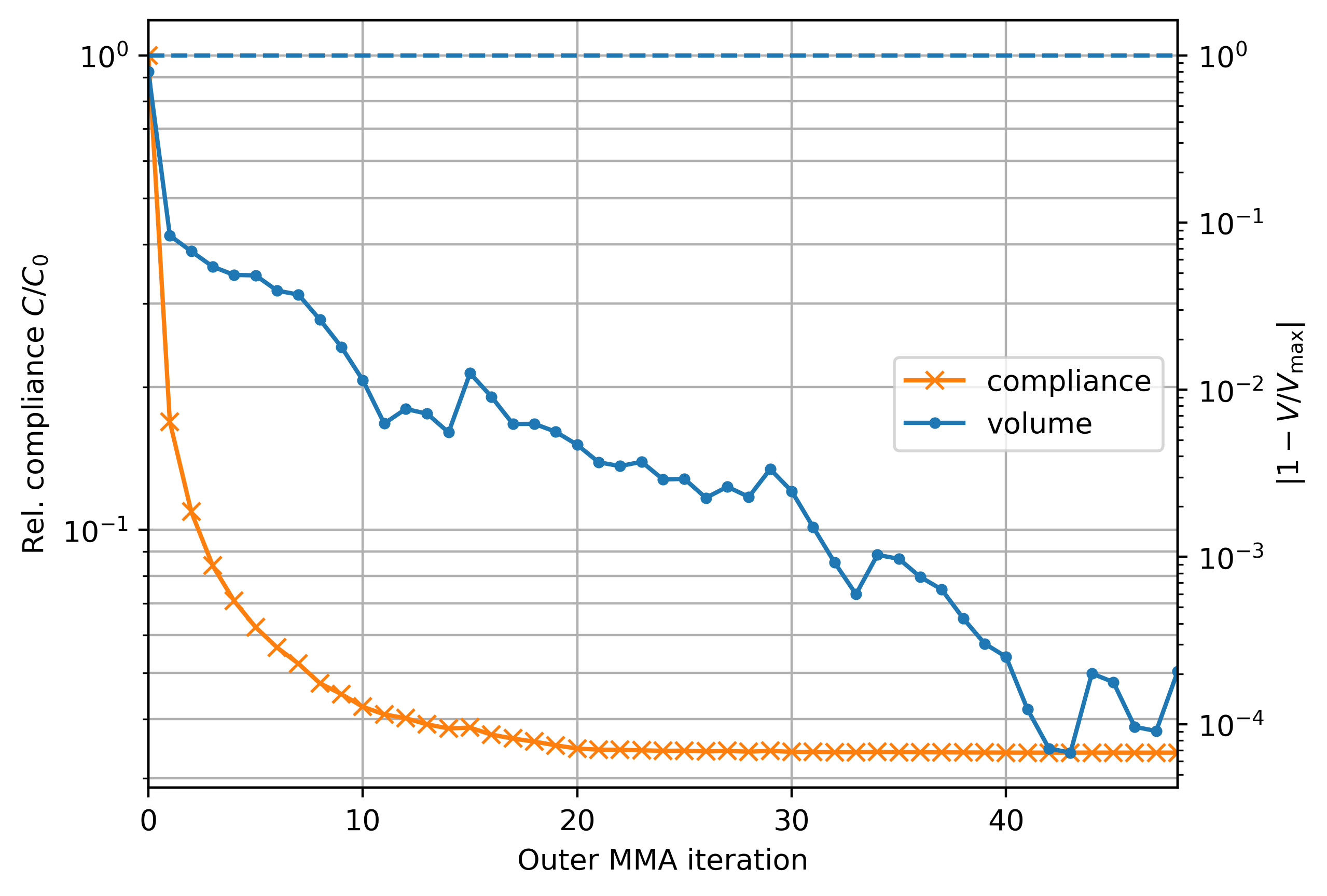
The deformed final design (displacement scaled by )
Source
pixels = dolfiny.pyvista.pixels
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[pixels, pixels // 2])
pv_grid.point_data[u.name] = u.x.array.reshape(-1, 3)
pv_grid.cell_data[s.name] = s.x.array
plotter.add_mesh(pv_grid.warp_by_vector(u.name, factor=5e3), color="black", line_width=1.5)
plotter.add_axes()
plotter.view_xy()
plotter.camera.elevation += 20
plotter.camera.zoom(2.0)
plotter.show()
plotter.close()
plotter.deep_clean()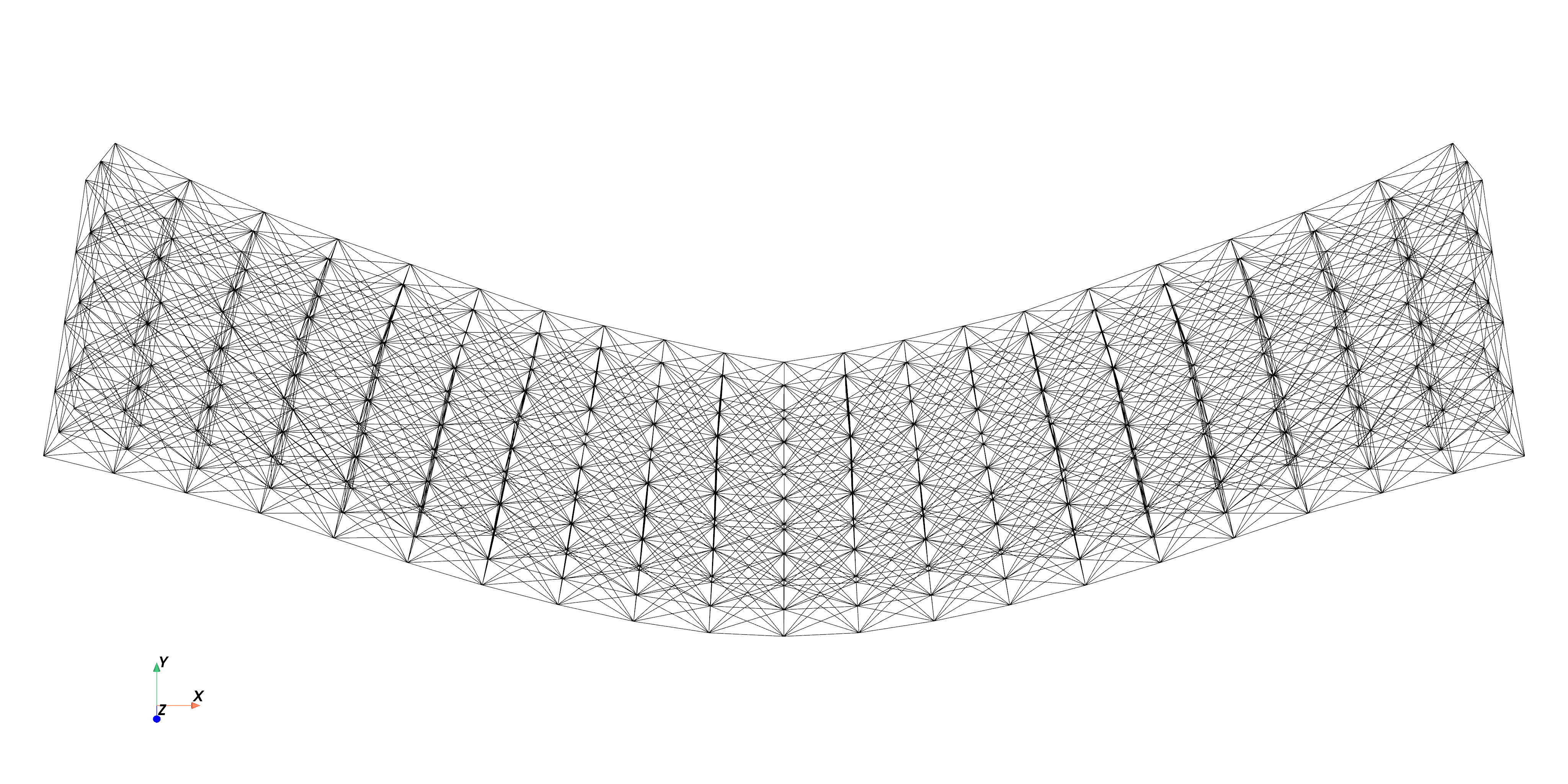
Visualisation of the optimised truss structure, each truss plotted corresponding to optimisation result (opacity of tubes according to ratio of maximal allowed cross sectional area). Radii are scaled by factor of 5, for visualisation purposes.
Source
plotter = pv.Plotter(window_size=[pixels, pixels // 2])
radius = np.sqrt(s.x.array / np.pi)
radius_max = np.sqrt(s_max / np.pi)
e_to_v = mesh.topology.connectivity(1, 0)
for e_idx in range(e_to_v.num_nodes):
a, b = e_to_v.links(e_idx)
plotter.add_mesh(
pv.Tube(
pointa=mesh.geometry.x[a],
pointb=mesh.geometry.x[b],
radius=radius[e_idx] * 5,
capping=True,
),
opacity=radius[e_idx] / radius_max,
)
plotter.add_axes()
plotter.view_xy()
plotter.camera.elevation += 20
plotter.camera.zoom(2.0)
plotter.show()
plotter.close()
plotter.deep_clean()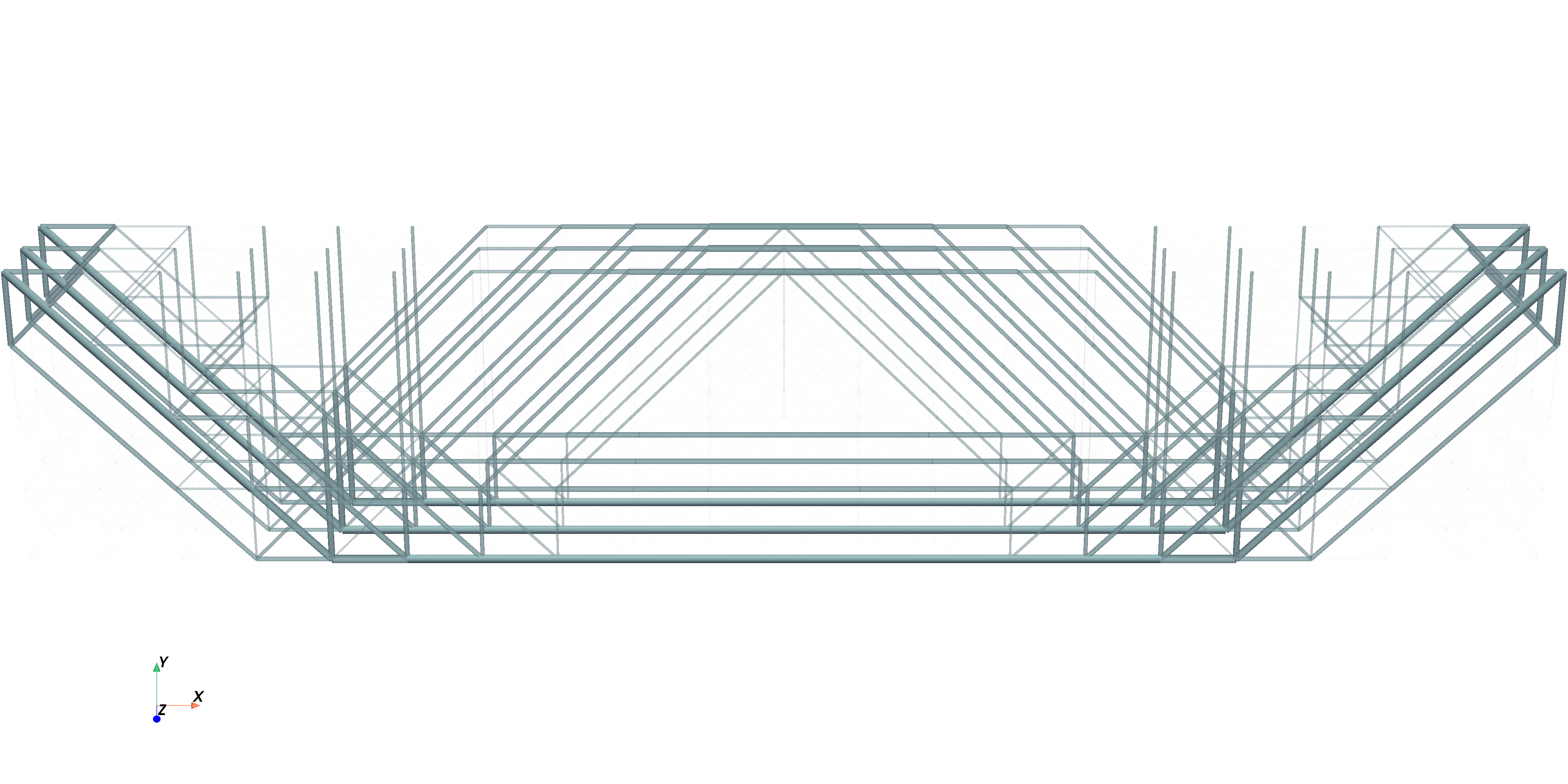
- Baratta, I. A., Dean, J. P., Dokken, J. S., Habera, M., Hale, J. S., Richardson, C. N., Rognes, M. E., Scroggs, M. W., Sime, N., & Wells, G. N. (2023). DOLFINx: The next generation FEniCS problem solving environment. Zenodo. 10.5281/zenodo.10447666
- Bleyer, J. (2024). Numerical tours of Computational Mechanics with FEniCSx (v0.2) [Computer software]. Zenodo. 10.5281/zenodo.13838486
- Christensen, P. W., & Klarbring, A. (2009). Sizing Stiffness Optimization of a Truss. In An Introduction to Structural Optimization (pp. 77–95). Springer Netherlands. 10.1007/978-1-4020-8666-3_5