This demo showcases how to define a solid hyperelastic material using eigenvalues of the Cauchy strain tensor.
In particular this demo emphasizes
symbolic computation of eigenvalues of a tensor field,
automatic differentiation of a strain energy function defined in terms of eigenvalues of the strain tensor.
The task is to find a displacement field which solves the variational problem (principle of virtual displacements)
for all . Stress tensor (second Piola-Kirchhoff) is computed from bulk and shear strain energies which are defined for a compressible Neo-Hookean material [Pence & Gou (2014)] as
with Cauchy strain tensor , deformation gradient and its derived invariants and and material parameters and .
For the hyperelastic material the strain energy is a potential for the stress tensor, i.e.
For isotropic strain energy functionals (which the Neo-Hookean model fulfils) we can write
for the three principal stresses (eigenvalues of the stress tensor ) and three principal stretches (eigenvalues of the strain tensor ) . Using the notion of principal stresses and stretches, the inner product contraction in the above variational problem simplifies to
The key point in the above is to express the strain energy functional purely in terms of principal stretches , which is achieved using
Principal stretches are available as symbolic closed-form expression of the primary unknown
displacement thanks to helper function dolfiny.invariants.eigenstate,
see [Habera & Zilian (2021)] for more detail.
Source
import argparse
from mpi4py import MPI
from petsc4py import PETSc
import basix
import dolfinx
import ufl
from dolfinx import default_scalar_type as scalar
import numpy as np
import pyvista
import sympy.physics.units as syu
import dolfiny
from dolfiny.units import Quantity
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description="Solid elasticity with classic or spectral formulation"
)
parser.add_argument(
"--formulation",
choices=["classic", "spectral"],
default="spectral",
help="Choose strain formulation: classic (Cauchy strain) or spectral (principal stretches)",
required=False,
)
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
def mesh_tube3d_gmshapi(
name="tube3d",
r=1.0,
t=0.2,
h=1.0,
nr=30,
nt=6,
nh=10,
x0=0.0,
y0=0.0,
z0=0.0,
do_quads=False,
order=1,
msh_file=None,
comm=MPI.COMM_WORLD,
):
"""
Create mesh of 3d tube using the Python API of Gmsh.
"""
tdim = 3 # target topological dimension
# Perform Gmsh work only on rank = 0
if comm.rank == 0:
import gmsh
# Initialise gmsh and set options
gmsh.initialize()
gmsh.option.setNumber("General.Terminal", 1)
gmsh.option.set_number("General.NumThreads", 1) # reproducibility
if do_quads:
gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.Algorithm", 8)
gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.Algorithm3D", 10)
# gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.SubdivisionAlgorithm", 2)
else:
gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.Algorithm", 5)
gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.Algorithm3D", 4)
gmsh.option.set_number("Mesh.AlgorithmSwitchOnFailure", 6)
# Add model under given name
gmsh.model.add(name)
# Create points and line
p0 = gmsh.model.occ.add_point(x0 + r, y0, 0.0)
p1 = gmsh.model.occ.add_point(x0 + r + t, y0, 0.0)
l0 = gmsh.model.occ.add_line(p0, p1)
s0 = gmsh.model.occ.revolve(
[(1, l0)],
x0,
y0,
z0,
0,
0,
1,
angle=+gmsh.pi,
numElements=[nr],
recombine=do_quads,
)
s1 = gmsh.model.occ.revolve(
[(1, l0)],
x0,
y0,
z0,
0,
0,
1,
angle=-gmsh.pi,
numElements=[nr],
recombine=do_quads,
)
ring, _ = gmsh.model.occ.fuse([s0[1]], [s1[1]])
tube = gmsh.model.occ.extrude(ring, 0, 0, h, [nh], recombine=do_quads) # noqa: F841
# Synchronize
gmsh.model.occ.synchronize()
# Get model entities
_points, _lines, surfaces, volumes = (gmsh.model.occ.get_entities(d) for d in [0, 1, 2, 3])
boundaries = gmsh.model.get_boundary(volumes, oriented=False) # noqa: F841
# Assertions, problem-specific
assert len(volumes) == 2
# Helper
def extract_tags(a):
return list(ai[1] for ai in a)
# Extract certain tags, problem-specific
tag_subdomains_total = extract_tags(volumes)
# Set geometrical identifiers (obtained by inspection)
tag_interfaces_lower = extract_tags([surfaces[0], surfaces[1]])
tag_interfaces_upper = extract_tags([surfaces[6], surfaces[9]])
tag_interfaces_inner = extract_tags([surfaces[2], surfaces[7]])
tag_interfaces_outer = extract_tags([surfaces[3], surfaces[8]])
# Define physical groups for subdomains (! target tag > 0)
domain = 1
gmsh.model.add_physical_group(tdim, tag_subdomains_total, domain)
gmsh.model.set_physical_name(tdim, domain, "domain")
# Define physical groups for interfaces (! target tag > 0)
surface_lower = 1
gmsh.model.add_physical_group(tdim - 1, tag_interfaces_lower, surface_lower)
gmsh.model.set_physical_name(tdim - 1, surface_lower, "surface_lower")
surface_upper = 2
gmsh.model.add_physical_group(tdim - 1, tag_interfaces_upper, surface_upper)
gmsh.model.set_physical_name(tdim - 1, surface_upper, "surface_upper")
surface_inner = 3
gmsh.model.add_physical_group(tdim - 1, tag_interfaces_inner, surface_inner)
gmsh.model.set_physical_name(tdim - 1, surface_inner, "surface_inner")
surface_outer = 4
gmsh.model.add_physical_group(tdim - 1, tag_interfaces_outer, surface_outer)
gmsh.model.set_physical_name(tdim - 1, surface_outer, "surface_outer")
# Set refinement in radial direction
gmsh.model.mesh.setTransfiniteCurve(l0, numNodes=nt)
# Generate the mesh
gmsh.model.mesh.generate()
# Set geometric order of mesh cells
gmsh.model.mesh.setOrder(order)
# Optional: Write msh file
if msh_file is not None:
gmsh.write(msh_file)
return gmsh.model if comm.rank == 0 else None, tdim
class Xdmf3Reader(pyvista.XdmfReader):
_vtk_module_name = "vtkIOXdmf3"
_vtk_class_name = "vtkXdmf3Reader"
def plot_tube3d_pyvista(u, s, comm=MPI.COMM_WORLD):
if comm.rank > 0:
return
grid = pyvista.UnstructuredGrid(*dolfinx.plot.vtk_mesh(u.function_space))
plotter = pyvista.Plotter(off_screen=True, theme=dolfiny.pyvista.theme)
plotter.add_axes()
plotter.enable_parallel_projection()
grid.point_data["u"] = u.x.array.reshape(-1, 3)
grid.point_data["von_mises"] = s.x.array / 1e6 # to MPa
grid_warped = grid.warp_by_vector("u", factor=1.0)
if not grid.get_cell(0).is_linear:
levels = 4
else:
levels = 0
s = plotter.add_mesh(
grid_warped.extract_surface(nonlinear_subdivision=levels),
scalars="von_mises",
scalar_bar_args={"title": "von Mises stress [MPa]"},
n_colors=10,
)
s.mapper.scalar_range = [0.0, 0.6]
plotter.add_mesh(
grid_warped.separate_cells()
.extract_surface(nonlinear_subdivision=levels)
.extract_feature_edges(),
style="wireframe",
color="black",
line_width=dolfiny.pyvista.pixels // 1000,
render_lines_as_tubes=True,
)
plotter.show_axes()
plotter.show()
plotter.close()
plotter.deep_clean()This demo is parametrised by the choice of formulation: “classic” or “spectral”. The “classic” formulation uses strain energy defined in terms of main invariants of the Cauchy strain tensor, while the “spectral” formulation uses strain energy defined in terms of the eigenvalues.
Source
print(f"Arguments: {args}")Arguments: Namespace(formulation='spectral')
Meshing, boundary tagging and function spaces definition¶
Mesh in this example is a tube with radius , thickness and height . It is tesselated using 27 node quadratic hexahedral elements.
Bottom of the tube is marked as “surface_lower” and top is marked as “surface_upper”.
name = f"solid_elasticity_{args.formulation}"
comm = MPI.COMM_WORLD
# Geometry and mesh parameters
r, t, h = 0.4, 0.1, 1
nr, nt, nh = 16, 5, 8
# Create the regular mesh of a tube with given dimensions
gmsh_model, tdim = mesh_tube3d_gmshapi(name, r, t, h, nr, nt, nh, do_quads=True, order=2)
# Get mesh and meshtags
mesh_data = dolfinx.io.gmsh.model_to_mesh(gmsh_model, comm, rank=0)
mesh = mesh_data.mesh
# Define shorthands for labelled tags
surface_lower = mesh_data.physical_groups["surface_lower"].tag
surface_upper = mesh_data.physical_groups["surface_upper"].tagOutput
Info : Meshing 1D...
Info : [ 0%] Meshing curve 1 (Line)
Info : [ 10%] Meshing curve 2 (Extruded)
Info : [ 20%] Meshing curve 3 (Extruded)
Info : [ 20%] Meshing curve 4 (Extruded)
Info : [ 30%] Meshing curve 5 (Extruded)
Info : [ 40%] Meshing curve 6 (Extruded)
Info : [ 40%] Meshing curve 7 (Extruded)
Info : [ 50%] Meshing curve 8 (Extruded)
Info : [ 60%] Meshing curve 9 (Extruded)
Info : [ 60%] Meshing curve 10 (Extruded)
Info : [ 70%] Meshing curve 11 (Extruded)
Info : [ 70%] Meshing curve 12 (Extruded)
Info : [ 80%] Meshing curve 13 (Extruded)
Info : [ 90%] Meshing curve 14 (Extruded)
Info : [ 90%] Meshing curve 15 (Extruded)
Info : [100%] Meshing curve 16 (Extruded)
Info : Done meshing 1D (Wall 0.000341331s, CPU 0.000313s)
Info : Meshing 2D...
Info : [ 0%] Meshing surface 1 (Extruded)
Info : [ 20%] Meshing surface 2 (Extruded)
Info : [ 30%] Meshing surface 3 (Extruded)
Info : [ 40%] Meshing surface 4 (Extruded)
Info : [ 50%] Meshing surface 5 (Extruded)
Info : [ 60%] Meshing surface 6 (Extruded)
Info : [ 70%] Meshing surface 7 (Extruded)
Info : [ 80%] Meshing surface 8 (Extruded)
Info : [ 90%] Meshing surface 9 (Extruded)
Info : [100%] Meshing surface 10 (Extruded)
Info : Done meshing 2D (Wall 0.00556887s, CPU 0.004621s)
Info : Meshing 3D...
Info : Meshing volume 1 (Extruded)
Info : Meshing volume 2 (Extruded)
Info : Done meshing 3D (Wall 0.0101648s, CPU 0.003963s)
Info : 1440 nodes 2040 elements
Info : Meshing order 2 (curvilinear on)...
Info : [ 0%] Meshing curve 1 order 2
Info : [ 10%] Meshing curve 2 order 2
Info : [ 10%] Meshing curve 3 order 2
Info : [ 20%] Meshing curve 4 order 2
Info : [ 20%] Meshing curve 5 order 2
Info : [ 20%] Meshing curve 6 order 2
Info : [ 30%] Meshing curve 7 order 2
Info : [ 30%] Meshing curve 8 order 2
Info : [ 30%] Meshing curve 9 order 2
Info : [ 40%] Meshing curve 10 order 2
Info : [ 40%] Meshing curve 11 order 2
Info : [ 40%] Meshing curve 12 order 2
Info : [ 50%] Meshing curve 13 order 2
Info : [ 50%] Meshing curve 14 order 2
Info : [ 60%] Meshing curve 15 order 2
Info : [ 60%] Meshing curve 16 order 2
Info : [ 60%] Meshing surface 1 order 2
Info : [ 70%] Meshing surface 2 order 2
Info : [ 70%] Meshing surface 3 order 2
Info : [ 70%] Meshing surface 4 order 2
Info : [ 80%] Meshing surface 5 order 2
Info : [ 80%] Meshing surface 6 order 2
Info : [ 80%] Meshing surface 7 order 2
Info : [ 90%] Meshing surface 8 order 2
Info : [ 90%] Meshing surface 9 order 2
Info : [ 90%] Meshing surface 10 order 2
Info : [100%] Meshing volume 1 order 2
Info : [100%] Meshing volume 2 order 2
Info : Done meshing order 2 (Wall 0.0422282s, CPU 0.028068s)
Quadrature rule is limited to the 4th degree for performance reasons. The symbolic expressions resulting from the eigenvalues of the Cauchy strain tensor are rather involved so the time to assemble the forms increases.
Function space discretisation is based on vector-valued isoparametric continuous Lagrange element with three components - since we model the displacement in three dimensions.
dx = ufl.Measure(
"dx", domain=mesh, subdomain_data=mesh_data.cell_tags, metadata={"quadrature_degree": 4}
)
ds = ufl.Measure(
"ds", domain=mesh, subdomain_data=mesh_data.facet_tags, metadata={"quadrature_degree": 4}
)
Ue = basix.ufl.element("P", mesh.basix_cell(), 2, shape=(mesh.geometry.dim,))
Uf = dolfinx.fem.functionspace(mesh, Ue)
print(f"Degrees-of-freedom per element: {Uf.element.space_dimension}")
# Define functions
u = dolfinx.fem.Function(Uf, name="u")
u_ = dolfinx.fem.Function(Uf, name="u_") # boundary conditions
δm = ufl.TestFunctions(ufl.MixedFunctionSpace(Uf))
(δu,) = δm
# Define state as (ordered) list of functions
m = [u]
# Functions for output / visualisation
vorder = mesh.geometry.cmap.degree
uo = dolfinx.fem.Function(dolfinx.fem.functionspace(mesh, ("P", vorder, (3,))), name="u")
so = dolfinx.fem.Function(dolfinx.fem.functionspace(mesh, ("P", vorder)), name="s") # for outputDegrees-of-freedom per element: 81
plot_tube3d_pyvista(uo, so)
Material parameters with units¶
There are four dimensional quantities in the problem:
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| reference length scale | ||
| load scale | ||
| shear modulus | ||
| bulk modulus |
derived from Poisson ratio , Lamé coefficient and Young’s modulus .
We can execute the Buckingham Pi analysis which shows overview of the dimensional quantities and derives a set of dimensionless numbers. In this examaple we arrive at two dimensionless numbers:
bulk-to-shear ratio and
loading factor .
nu = 0.4
E = Quantity(mesh, 1, syu.mega * syu.pascal, "E") # Young's modulus
mu = Quantity(mesh, E.scale / (2 * (1 + nu)), syu.mega * syu.pascal, "μ") # shear modulus
λ = Quantity(
mesh, E.scale * nu / ((1 + nu) * (1 - 2 * nu)), syu.mega * syu.pascal, "λ"
) # Lamé constant
kappa = Quantity(mesh, λ.scale + 2 / 3 * mu.scale, syu.mega * syu.pascal, "κ") # Lamé constant
l_ref = Quantity(mesh, 0.1, syu.meter, "l_ref")
t_ref = Quantity(mesh, 0.2, syu.mega * syu.pascal, "t_ref")
quantities = [l_ref, t_ref, mu, kappa]
quantities = [mu, kappa, l_ref, t_ref]
if comm.rank == 0:
dolfiny.units.buckingham_pi_analysis(quantities)
==================================================
Buckingham Pi Analysis
==================================================
Symbol | Expression | Value (in base units)
-------+-----------------+------------------------------------
μ | 3.571e+5*pascal | 3.571e+5*kilogram/(meter*second**2)
κ | 1.667e+6*pascal | 1.667e+6*kilogram/(meter*second**2)
l_ref | 0.1*meter | 0.1*meter
t_ref | 2.0e+5*pascal | 2.0e+5*kilogram/(meter*second**2)
Dimension matrix (7 × 4):
Dimension | μ | κ | l_ref | t_ref
--------------------+----+----+-------+------
amount_of_substance | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0
current | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0
length | -1 | -1 | 1 | -1
luminous_intensity | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0
mass | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1
temperature | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0
time | -2 | -2 | 0 | -2
Dimensionless groups (2):
Group | Expression | Value
------+------------+------
Pi_1 | κ/μ | 4.67
Pi_2 | t_ref/μ | 0.56
==================================================
Weak form¶
F = ufl.Identity(3) + ufl.grad(u)
# Strain measure: Cauchy strain tensor
C = F.T * F
C = ufl.variable(C)
def strain_energy_bulk(i1, i2, i3):
J = ufl.sqrt(i3)
return kappa / 2 * (J - 1) ** 2
def strain_energy_shear(i1, i2, i3):
J = ufl.sqrt(i3)
return mu / 2 * (i1 - 3 - 2 * ufl.ln(J))
def von_mises_stress(S):
return ufl.sqrt(3 / 2 * ufl.inner(ufl.dev(S), ufl.dev(S)))
# Formulation-specific strain measures
if args.formulation == "spectral":
c, _ = dolfiny.invariants.eigenstate(C)
c = ufl.as_vector(c)
c = ufl.variable(c)
# Reconstruct the principal invariants from the principal stretches
i1, i2, i3 = c[0] + c[1] + c[2], c[0] * c[1] + c[1] * c[2] + c[0] * c[2], c[0] * c[1] * c[2]
δC = ufl.derivative(c, m, δm)
S_bulk = 2 * ufl.diff(strain_energy_bulk(i1, i2, i3), c)
S_shear = 2 * ufl.diff(strain_energy_shear(i1, i2, i3), c)
S = S_bulk + S_shear
svm = von_mises_stress(ufl.diag(S))
elif args.formulation == "classic":
δC = ufl.derivative(C, m, δm)
i1, i2, i3 = dolfiny.invariants.invariants_principal(C)
S_bulk = 2 * ufl.diff(strain_energy_bulk(i1, i2, i3), C)
S_shear = 2 * ufl.diff(strain_energy_shear(i1, i2, i3), C)
S = S_bulk + S_shear
svm = von_mises_stress(S)
else:
raise RuntimeError(f"Unknown formulation '{args.formulation}'")Boundary traction is created to represent rotational vector field in the shifted -plane which is scaled with the reference load scale . We first compute radial vector field in the shifted -plane
which we normalize and cross product with the unit vector ,
A load factor is increased from 0 to 1 during the loading procedure.
x0 = ufl.SpatialCoordinate(mesh)
load_factor = dolfinx.fem.Constant(mesh, scalar(0.0))
ez = ufl.as_vector([0.0, 0.0, 1.0])
d = x0 - l_ref * h * ez
d /= ufl.sqrt(ufl.inner(d, d))
t = ufl.cross(d, ez) * t_ref * load_factor
mapping = {
mesh.ufl_domain(): l_ref,
u: l_ref * u,
δu: l_ref * δu,
}
terms = {
"int_bulk": -1 / 2 * ufl.inner(δC, S_bulk) * dx,
"int_shear": -1 / 2 * ufl.inner(δC, S_shear) * dx,
"external": ufl.inner(δu, t) * ds(surface_upper),
}
factorized = dolfiny.units.factorize(terms, quantities, mode="factorize", mapping=mapping)
assert isinstance(factorized, dict)
dimsys = syu.si.SI.get_dimension_system()
assert dimsys.equivalent_dims(
dolfiny.units.get_dimension(terms["int_bulk"], quantities, mapping),
syu.energy,
)
assert dimsys.equivalent_dims(
dolfiny.units.get_dimension(strain_energy_bulk(i1, i2, i3), quantities, mapping),
syu.energy * syu.length**-3,
)
assert dimsys.equivalent_dims(
dolfiny.units.get_dimension(S_shear, quantities, mapping),
syu.pressure,
)
reference_term = "int_bulk"
ref_factor = factorized[reference_term].factor
normalized = dolfiny.units.normalize(factorized, reference_term, quantities)
form = sum(normalized.values(), ufl.form.Zero())
# Overall form (as list of forms)
forms = ufl.extract_blocks(form) # type: ignore
==================================================
Terms after normalization with "int_bulk"
==================================================
Reference factor from 'int_bulk':
Term | Factor | Value (in base units)
---------+------------+-----------------------------------
int_bulk | l_ref**3*κ | 1667.0*kilogram*meter**2/second**2
Term | Factor | Value (in base units)
----------+---------+----------------------
int_bulk | 1 | 1.000
int_shear | μ/κ | 0.2143
external | t_ref/κ | 0.1200
==================================================
The problem solved leads to symmetric positive definite system on the algebraic level. We choose to solve it using MUMPS Cholesky solver for general symmetric matrices. We explicitly numerical pivoting by setting CNTL(1) = 0.
The nonlinear SNES solver is configured to use Newton line search with no (basic) line search.
opts = PETSc.Options(name) # type: ignore[attr-defined]
opts["snes_type"] = "newtonls"
opts["snes_linesearch_type"] = "basic"
opts["snes_rtol"] = 1.0e-08
opts["snes_max_it"] = 10
opts["ksp_type"] = "preonly"
opts["pc_type"] = "cholesky"
opts["pc_factor_mat_solver_type"] = "mumps"
opts["mat_mumps_cntl_1"] = 0.0Source
# FFCx options (formulation-specific)
if args.formulation == "spectral":
# ARM64-specific optimizations for spectral formulation
jit_options = dict(
cffi_extra_compile_args=[
"-fdisable-rtl-combine",
"-fno-schedule-insns",
"-fno-schedule-insns2",
]
)
else:
# Standard options for classic formulation
jit_options = dict(cffi_extra_compile_args=["-g0"])
# Create nonlinear problem: SNES
problem = dolfiny.snesproblem.SNESProblem(forms, m, prefix=name, jit_options=jit_options)
# Identify dofs of function spaces associated with tagged interfaces/boundaries
b_dofs_Uf = dolfiny.mesh.locate_dofs_topological(Uf, mesh_data.facet_tags, surface_lower)
# Set/update boundary conditions
problem.bcs = [
dolfinx.fem.dirichletbc(u_, b_dofs_Uf), # u lower face
]Output
cc1: note: disable pass rtl-combine for functions in the range of [0, 4294967295]
cc1: note: disable pass rtl-combine for functions in the range of [0, 4294967295]
libffcx_forms_f21be39306dba31b5c1eacc1276bb1e76c7fcc0b.c: In function ‘tabulate_tensor_integral_ec0dd4e87072e207b54b2373929051a04566187f_hexahedron’:
libffcx_forms_f21be39306dba31b5c1eacc1276bb1e76c7fcc0b.c:598:6: note: variable tracking size limit exceeded with ‘-fvar-tracking-assignments’, retrying without
598 | void tabulate_tensor_integral_ec0dd4e87072e207b54b2373929051a04566187f_hexahedron(double* restrict A,
| ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
# Apply external force via load stepping
for lf in np.linspace(0.0, 1.0, 10 + 1)[1:]:
# Set load factor
load_factor.value = lf
dolfiny.utils.pprint(f"\n*** Load factor = {lf:.4f} ({args.formulation} formulation) \n")
# Solve nonlinear problem
problem.solve()
# Assert convergence of nonlinear solver
problem.status(verbose=True, error_on_failure=True)
# Assert symmetry of operator
assert dolfiny.la.is_symmetric(problem.J)
# Interpolate for output purposes
dolfiny.interpolation.interpolate(u, uo)
dolfiny.interpolation.interpolate(svm, so)
# Write results to file
with dolfiny.io.XDMFFile(comm, f"{name}.xdmf", "w") as ofile:
ofile.write_mesh_meshtags(mesh)
ofile.write_function(uo)
ofile.write_function(so)Output
*** Load factor = 0.1000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=0.000e+00 |dx|=0.000e+00 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=0.000e+00 |dx|=0.000e+00 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.131e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.355e+00 |dx|=3.355e+00 |r|=1.258e-03 (u)
# all |x|=3.355e+00 |dx|=3.355e+00 |r|=1.258e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.258e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.054e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.256e+00 |dx|=1.644e-01 |r|=2.691e-05 (u)
# all |x|=3.256e+00 |dx|=1.644e-01 |r|=2.691e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.691e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=7.186e-18
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=4.947e-02 |r|=9.646e-06 (u)
# all |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=4.947e-02 |r|=9.646e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=9.646e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.271e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=9.594e-04 |r|=4.645e-09 (u)
# all |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=9.594e-04 |r|=4.645e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.645e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=8.872e-22
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=6.808e-06 |r|=2.275e-13 (u)
# all |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=6.808e-06 |r|=2.275e-13
absolute asymmetry measure = 3.561e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 9.104e-17
*** Load factor = 0.2000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=6.808e-06 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=3.253e+00 |dx|=6.808e-06 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.211e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.563e+00 |dx|=3.312e+00 |r|=1.472e-03 (u)
# all |x|=6.563e+00 |dx|=3.312e+00 |r|=1.472e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.472e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.677e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.615e+00 |dx|=1.439e-01 |r|=2.808e-05 (u)
# all |x|=6.615e+00 |dx|=1.439e-01 |r|=2.808e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.808e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=9.534e-18
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.664e+00 |dx|=7.284e-02 |r|=1.491e-05 (u)
# all |x|=6.664e+00 |dx|=7.284e-02 |r|=1.491e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.491e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.737e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.429e-03 |r|=8.404e-09 (u)
# all |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.429e-03 |r|=8.404e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=8.404e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.809e-21
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.503e-05 |r|=9.099e-13 (u)
# all |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.503e-05 |r|=9.099e-13
absolute asymmetry measure = 3.632e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 8.800e-17
*** Load factor = 0.3000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.503e-05 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=6.665e+00 |dx|=1.503e-05 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.607e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.020e+01 |dx|=3.547e+00 |r|=2.479e-03 (u)
# all |x|=1.020e+01 |dx|=3.547e+00 |r|=2.479e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.479e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.762e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.026e+01 |dx|=1.653e-01 |r|=4.638e-05 (u)
# all |x|=1.026e+01 |dx|=1.653e-01 |r|=4.638e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.638e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.155e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=9.295e-02 |r|=2.039e-05 (u)
# all |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=9.295e-02 |r|=2.039e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.039e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=4.121e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=3.342e-03 |r|=3.430e-08 (u)
# all |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=3.342e-03 |r|=3.430e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=3.430e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=6.136e-21
# SNES iteration 5
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=5.170e-05 |r|=8.867e-12 (u)
# all |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=5.170e-05 |r|=8.867e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 0 |r|=8.867e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.548e-25
# SNES iteration 6 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=1.307e-09 |r|=3.117e-16 (u)
# all |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=1.307e-09 |r|=3.117e-16
absolute asymmetry measure = 4.230e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 9.457e-17
*** Load factor = 0.4000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=1.307e-09 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=1.033e+01 |dx|=1.307e-09 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.914e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.413e+01 |dx|=3.827e+00 |r|=4.048e-03 (u)
# all |x|=1.413e+01 |dx|=3.827e+00 |r|=4.048e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.048e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.633e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.415e+01 |dx|=1.850e-01 |r|=1.075e-04 (u)
# all |x|=1.415e+01 |dx|=1.850e-01 |r|=1.075e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.075e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=8.188e-18
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=5.544e-02 |r|=7.397e-06 (u)
# all |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=5.544e-02 |r|=7.397e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=7.397e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=6.310e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=4.906e-03 |r|=6.294e-08 (u)
# all |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=4.906e-03 |r|=6.294e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=6.294e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.265e-21
# SNES iteration 5
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=2.603e-05 |r|=1.940e-12 (u)
# all |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=2.603e-05 |r|=1.940e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.940e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.556e-25
# SNES iteration 6 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=1.247e-09 |r|=4.199e-16 (u)
# all |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=1.247e-09 |r|=4.199e-16
absolute asymmetry measure = 3.969e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 8.406e-17
*** Load factor = 0.5000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=1.247e-09 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=1.419e+01 |dx|=1.247e-09 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=4.178e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.808e+01 |dx|=3.946e+00 |r|=5.126e-03 (u)
# all |x|=1.808e+01 |dx|=3.946e+00 |r|=5.126e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=5.126e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.595e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.804e+01 |dx|=1.959e-01 |r|=1.674e-04 (u)
# all |x|=1.804e+01 |dx|=1.959e-01 |r|=1.674e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.674e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.683e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=5.355e-02 |r|=1.606e-06 (u)
# all |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=5.355e-02 |r|=1.606e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.606e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.012e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.289e-03 |r|=1.538e-08 (u)
# all |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.289e-03 |r|=1.538e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.538e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.856e-22
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.299e-06 |r|=2.198e-14 (u)
# all |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.299e-06 |r|=2.198e-14
absolute asymmetry measure = 4.493e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 9.415e-17
*** Load factor = 0.6000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.299e-06 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=1.799e+01 |dx|=2.299e-06 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=4.139e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.169e+01 |dx|=3.782e+00 |r|=4.790e-03 (u)
# all |x|=2.169e+01 |dx|=3.782e+00 |r|=4.790e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.790e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.546e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.160e+01 |dx|=1.899e-01 |r|=1.478e-04 (u)
# all |x|=2.160e+01 |dx|=1.899e-01 |r|=1.478e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.478e-04
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.359e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=9.993e-02 |r|=1.152e-05 (u)
# all |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=9.993e-02 |r|=1.152e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.152e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=9.073e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=6.437e-03 |r|=1.124e-07 (u)
# all |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=6.437e-03 |r|=1.124e-07
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.124e-07
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=6.275e-21
# SNES iteration 5
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=4.364e-05 |r|=6.216e-12 (u)
# all |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=4.364e-05 |r|=6.216e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 0 |r|=6.216e-12
# SNES iteration 5, KSP iteration 1 |r|=4.582e-25
# SNES iteration 6 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=3.058e-09 |r|=5.852e-16 (u)
# all |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=3.058e-09 |r|=5.852e-16
absolute asymmetry measure = 5.568e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 9.454e-17
*** Load factor = 0.7000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=3.058e-09 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=2.150e+01 |dx|=3.058e-09 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.893e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.483e+01 |dx|=3.441e+00 |r|=3.670e-03 (u)
# all |x|=2.483e+01 |dx|=3.441e+00 |r|=3.670e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=3.670e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.345e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.471e+01 |dx|=1.720e-01 |r|=9.135e-05 (u)
# all |x|=2.471e+01 |dx|=1.720e-01 |r|=9.135e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=9.135e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.428e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=9.648e-02 |r|=1.270e-05 (u)
# all |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=9.648e-02 |r|=1.270e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.270e-05
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=6.064e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=3.682e-03 |r|=3.581e-08 (u)
# all |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=3.682e-03 |r|=3.581e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=3.581e-08
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.971e-21
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=2.313e-05 |r|=1.603e-12 (u)
# all |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=2.313e-05 |r|=1.603e-12
absolute asymmetry measure = 5.332e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 7.986e-17
*** Load factor = 0.8000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=2.313e-05 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=2.462e+01 |dx|=2.313e-05 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.807e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.757e+01 |dx|=3.072e+00 |r|=2.624e-03 (u)
# all |x|=2.757e+01 |dx|=3.072e+00 |r|=2.624e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.624e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=3.612e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.744e+01 |dx|=1.506e-01 |r|=5.122e-05 (u)
# all |x|=2.744e+01 |dx|=1.506e-01 |r|=5.122e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=5.122e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.050e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=7.118e-02 |r|=6.890e-06 (u)
# all |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=7.118e-02 |r|=6.890e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=6.890e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=2.953e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=1.353e-03 |r|=4.565e-09 (u)
# all |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=1.353e-03 |r|=4.565e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.565e-09
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.086e-20
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=3.959e-06 |r|=4.078e-14 (u)
# all |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=3.959e-06 |r|=4.078e-14
absolute asymmetry measure = 5.489e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 7.664e-17
*** Load factor = 0.9000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=3.959e-06 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=2.738e+01 |dx|=3.959e-06 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.130e-15
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.999e+01 |dx|=2.745e+00 |r|=1.889e-03 (u)
# all |x|=2.999e+01 |dx|=2.745e+00 |r|=1.889e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.889e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.677e-17
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.988e+01 |dx|=1.296e-01 |r|=2.962e-05 (u)
# all |x|=2.988e+01 |dx|=1.296e-01 |r|=2.962e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.962e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.085e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.715e-02 |r|=2.732e-06 (u)
# all |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.715e-02 |r|=2.732e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=2.732e-06
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.013e-19
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.517e-04 |r|=4.578e-10 (u)
# all |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.517e-04 |r|=4.578e-10
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.578e-10
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.637e-22
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.690e-07 |r|=8.968e-16 (u)
# all |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.690e-07 |r|=8.968e-16
absolute asymmetry measure = 6.142e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 8.227e-17
*** Load factor = 1.0000 (spectral formulation)
# SNES iteration 0
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.690e-07 |r|=1.653e-04 (u)
# all |x|=2.984e+01 |dx|=4.690e-07 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.653e-04
# SNES iteration 0, KSP iteration 1 |r|=8.300e-16
# SNES iteration 1
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.218e+01 |dx|=2.475e+00 |r|=1.408e-03 (u)
# all |x|=3.218e+01 |dx|=2.475e+00 |r|=1.408e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.408e-03
# SNES iteration 1, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.341e-16
# SNES iteration 2
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.208e+01 |dx|=1.103e-01 |r|=1.807e-05 (u)
# all |x|=3.208e+01 |dx|=1.103e-01 |r|=1.807e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 0 |r|=1.807e-05
# SNES iteration 2, KSP iteration 1 |r|=7.923e-17
# SNES iteration 3
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=3.044e-02 |r|=9.974e-07 (u)
# all |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=3.044e-02 |r|=9.974e-07
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 0 |r|=9.974e-07
# SNES iteration 3, KSP iteration 1 |r|=5.570e-20
# SNES iteration 4
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=1.577e-04 |r|=4.883e-11 (u)
# all |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=1.577e-04 |r|=4.883e-11
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 0 |r|=4.883e-11
# SNES iteration 4, KSP iteration 1 |r|=1.548e-23
# SNES iteration 5 success = CONVERGED_FNORM_RELATIVE
# sub 0 [ 29k] |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=5.559e-08 |r|=8.004e-16 (u)
# all |x|=3.206e+01 |dx|=5.559e-08 |r|=8.004e-16
absolute asymmetry measure = 5.453e-16
relative asymmetry measure = 7.097e-17
plot_tube3d_pyvista(uo, so)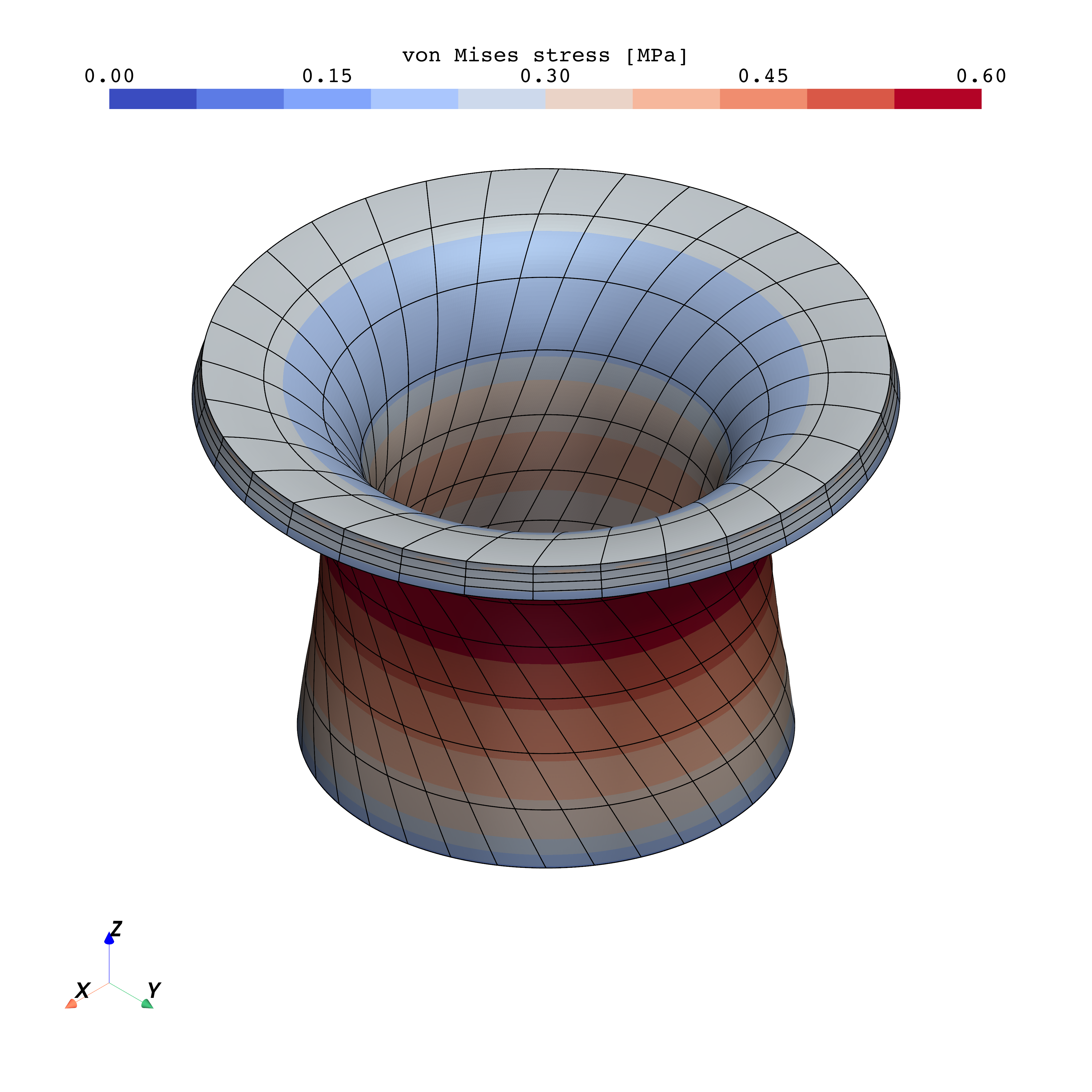
- Pence, T. J., & Gou, K. (2014). On compressible versions of the incompressible neo-Hookean material. Mathematics and Mechanics of Solids, 20(2), 157–182. 10.1177/1081286514544258
- Habera, M., & Zilian, A. (2021). Symbolic spectral decomposition of 3x3 matrices. arXiv. 10.48550/ARXIV.2111.02117